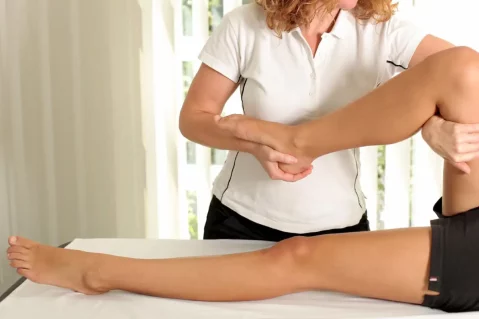
Physiotherapy is a front-line healthcare discipline. It is involved in the prevention and promotion of health, and the assessment, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of impairments and disabilities affecting a person’s neurological, musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems. It uses a variety of modalities such as manual therapy, heat, cryotherapy (cold), electrotherapy (muscle/sensory stimulation, ultrasound, laser, etc.), hydrotherapy (water), exercises, ultrasound graphy for sensory feedback. Such rehabilitation includes neuro-musculoskeletal problems, i.e. neurological, articular, muscular, balance, coordination, sensitivity, strength, endurance, pain and proprioception problems. The physiotherapist’s aim is to bring the patient back to normal or even optimal physical fitness.
Physiotherapy is adapted to the injuries inherent in everyday life or sport practice, as well as to the requirements and technical characteristics of each sportsperson and their sport or lifestyle.
Physiotherapy treats disorders of the musculoskeletal system such as :
- Muscle pain (strains, tears, contractures, atrophy, hypertrophy)
- Tendon pain
- Nerve pain (tingling, paresthesia, burning, freezing)
- Ligament pain (torn, ruptured)
- Bone pain
- Arm pain / fracture
- Neck Pain / Fracture
- Pain / Back fracture
- Shoulder pain / fracture
- Head and skull pain
- Pain / Hip fracture
- Pain / Coccyx fracture
- Pain / Sacrum-Iliac fracture
- Pain / Fracture Knee
- Pain / Fracture Meniscus
- Pain / Fracture Ankle
- Pain / Fracture Foot
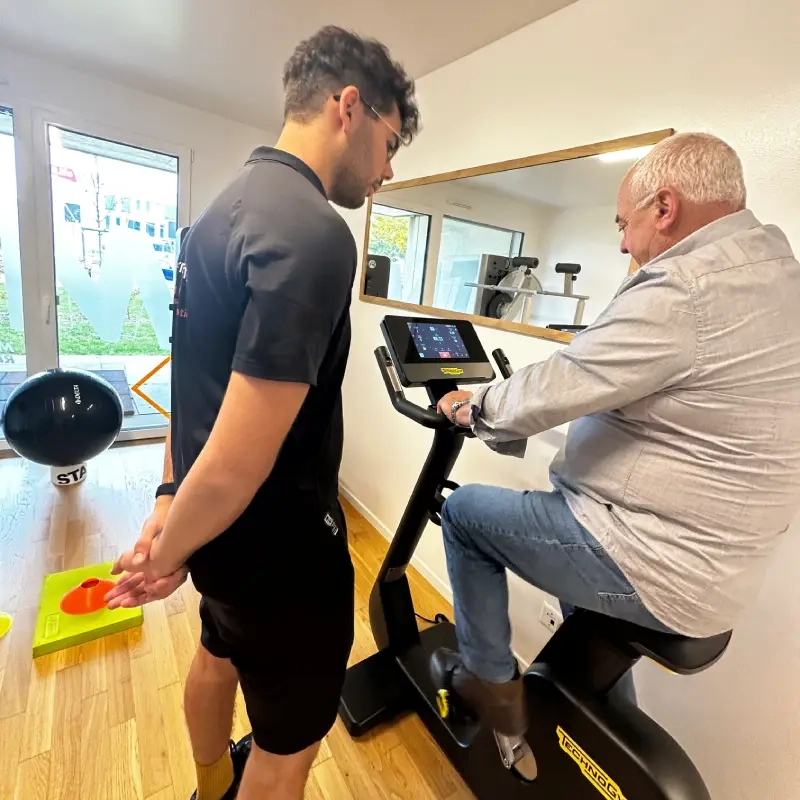
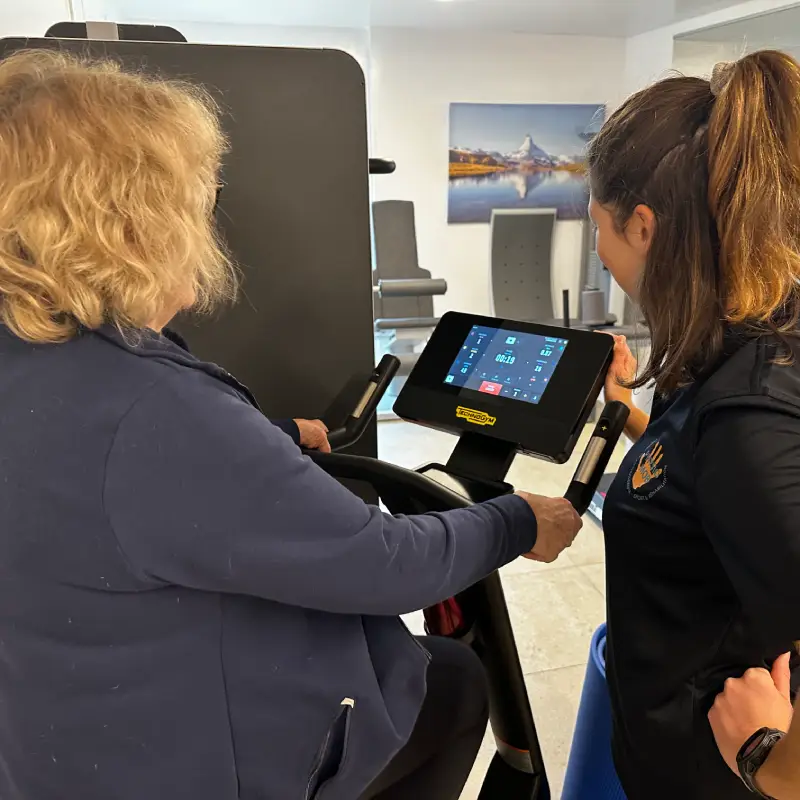


And more specifically
- Lumbar and back problems (osteoarthritis, herniated disc, dysfunction, pain, sciatica, etc.)
- Ankle/knee sprains (rupture/strain of LLI; LLE; ACL; Meniscus)
- Cervical problems (pain, joint dysfunction, osteoarthritis, brachialgia, hernia, headaches, whiplash, migraine, headache, vertigo, imbalance)
- Cervicalgia
- Back pain
- Low back pain
- Lumbago
- Sciatica
- Lumbosciatica
- Discarthrosis
- Disc disease
- Herniated Disc
- Tendonitis (epicondylitis, epitrochleitis, tennis elbow, golf elbow jumper’s knee, osgood schlatter)
- Bursitis
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
- Sprains, ligament tears, windscreen wipers,
- Muscle strain
- Patellofemoral syndrome (chondromalacia)
- Muscle imbalance
- Post-op rehabilitation
- Post-immobilisation rehabilitation
- Loss of function due to osteoarthritis
- Tibial periostitis
- Plantar fasciitis, Lenoi’s spine
- Trigger point
- Trigger point
- Posturology